January 2023 Update:
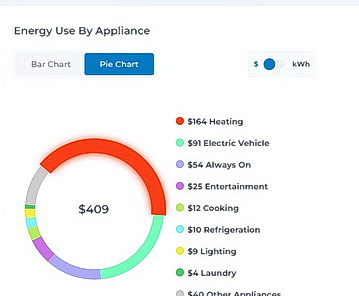
Long Island’s electric utility company can now provide a breakdown of electricl charges by appliance, and that includes home EV charging.
If you live in Long Island and use PSEGLI, you can contact them to find out how much your charging cost are.
They also offer different rate packages based on the time each appliance is used, called Time of Use (TOU). If you’d like to learn more about EVs and charging, keep reading.
EV Overview

Electric cars, also known as electric vehicles or EVs, have taken the auto world by storm. These vehicles are powered by electricity and not gasoline. Because of this, they produce zero CO2 emissions when driven — unlike gas-powered cars. These eco-friendly cars are growing in popularity because of their positive impact on the environment and the savings in gasoline costs.
The demand for electric cars will continue to rise due to government initiatives and growing awareness among consumers regarding the benefits of switching to an EV. If you’re thinking of buying an EV soon, you might be wondering how much it costs to charge an EV battery and just how much that will add to your monthly expenses. In this blog post, we explore everything you need to know about charging an EV battery and its cost.
What is an Electric Vehicle?
An electric vehicle, or EV, is a vehicle that uses electricity as its source of power. This type of vehicle uses an electric motor as its source of propulsion instead of a gasoline engine. There are several types of EVs, including hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs), plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs), and battery electric vehicles (BEVs). EVs can be powered by solar energy, wind energy, or an electrical outlet at home. The Advantages of Driving an EV: There are a number of benefits to driving an electric vehicle, including the following: – You don’t face the risk of CO2 emissions. – They’re cheaper to maintain and repair. – They produce almost no noise pollution. – They’re a lot more energy efficient. – You can save money on fuel costs.
The Disadvantages of Driving an EV: While driving an electric vehicle comes with a range of benefits, it also has some disadvantages, including the following:
- The high initial cost of EVs.
- The limited distance that can be driven on a single charge.
- Lack of charging station infrastructure in some regions.
- Slower recharging time compared to gasoline-powered cars.
- Limited availability of models.
- Lack of knowledge about EVs among car dealers
- Lack of awareness about the benefits of EVs.
How Much Does it Cost to Charge an EV Battery?

The cost to charge an EV battery mainly depends on a few factors, including the type of EV, the current electricity rate, and the distance you need to travel. Electricity rates vary around the country, and you can check the rates and plans offered by your local utility company. You can also use an online tool like the “Electricity Cost Calculator” tool provided by the Department of Energy to get an idea of how much electricity costs in your area.
The distance that you need to travel also factors into the cost to charge an EV battery. The further you have to travel, the more it will cost to charge the vehicle’s battery. You can check the miles per gallon equivalent (MPGe) on your EV’s sticker or the car’s official website to get an idea of how many miles you can travel with a full charge. The type of EV you own and the current charging method you’re using also add to the cost of charging the battery. Plug-in hybrid electric vehicles, for example, tend to cost more to charge than battery electric vehicles.
How Long Does it Take to Charge an Electric Vehicle Battery?
This depends on a few factors, including the type of EV you own, the current charging method, and your electricity rate. Plug-in hybrid electric vehicles tend to charge faster than battery electric vehicles, but you can use the following charging times as a general guide: – An average full charge takes approximately 10 hours. – A fast charge takes approximately 30 minutes. – A rapid charge takes approximately 15 minutes. You can also check your EV’s manual or the car’s official website to get the charging times specific to your vehicle.
Where are Chargers for EVs Located?

As President Biden’s infrastructure bill goes into effect, you can expect more and more EV charging portals to materialize. They will be along highways, main roads, parking lots and garages as well as housing development communities and other locations. You may have already noticed EV portals where you are.
In Nassau County, some parking lots already have them such as the Stop and Shop lots that are located throughout the county. Some Long Island town garages have installed them as well. So expect more to be installed we move forward with the EV phenomenon.
What is the Difference Between Level 1 and Level 2 Chargers?

There are some major differences. A level 1 charger can be plugged into any 110 volt outlet, but charges at about twice as long as a level 2 charger, which connects to a 220/240 volt outlet. If you recall our article on voltage, it is the amount of current that is ‘pushed’ out. Like a water faucet. The more you move the lever, the faster the water comes out. So a level 1 charger which uses 110 volts, the amount of current is, on average 15 amps. A level 2 charger can draw up to 60 amps, depending on the size of the breaker in the house.
Tips to Avoid High Electricity Costs When Charging an EV
If you’re worried about the high electricity costs associated with charging your EV battery, there are a few things you can do to minimize them, including the following:
- Choose the right EV charging method. For example, plug-in hybrids can be charged using standard 110/120-volt wall outlets, and battery electric vehicles can be charged using 220-volt outlets.
- Charge your EV during off-peak hours. Most utility companies offer cheaper rates off-peak hours, usually during nighttime. In Long Island, PSEGLI offers a Time of Use (TOU) plan that may be beneficial depending upon the time you use most of your home electricity.
- Charge your EV at work. Some employers offer EV charging stations for their employees, which you can use to charge your EV during working hours.
- Don’t charge your EV if you don’t have to, but driving your EV until the battery is very low before charging it is not recommended.
Note: Most electric Vehicles are set up to charge to 80% of battery capacity. This is because continuous charging to 100% can reduce the battery life.
Conclusion

An electric vehicle, or EV, is a vehicle that uses electricity as its source of power. EVs can be powered by solar energy, wind energy, or an electrical outlet at home or on the road.
The advantages of driving an EV:
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- – You don’t face the risk of CO2 emissions.
- – They’re cheaper to maintain and repair.
- – They produce almost no noise pollution.
- – They’re a lot more energy efficient.
- – You can save money on fuel costs.
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
The Disadvantages of Driving an EV:
- The high initial cost of EVs.
- The limited distance that can be driven on a single charge. –
- A lack of charging station infrastructure in some regions. –
- A slower recharging time compared to gasoline-powered cars. The cost to charge an EV battery mainly depends on a few factors, including the type of EV you own, the current electricity rate, and the distance you need to travel. The time it takes to charge an EV battery depends on a few factors, including the type of EV you own, the current charging method, and your electricity rate.
With that said, if you don’t already have an EV, but want to get one, keep a watchful eye out as the technology of EVs develop, as well as the infrastructure where more and more charging stations will be installed throughout the United States.